It is important for a business to have a comprehensive view of its performance in order to achieve its future goals. Therefore, every business prepares financial statements to determine its actual financial position. To understand financial statements, their types and more details, read further.
You will Learn About:
What is a financial statement?

Financial statements act as the transcript of a business. They depict the profitability, ownership structure, financial position, and liquidity status of the business.
The four major types of financial statements are- statements of profit and loss, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and statements of change in equity.
The preparation of financial statements is guided by a set of accounting principles and methods. For example, General Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) have four basic principles- objectivity, materiality, prudence, and consistency. On the other hand, International Finance Reporting Standards (IFRS) have four basic principles- clarity, reliability, relevance, and comparability.
Return on equity: Highlights
- Financial statements are written records that show the financial performance of the business.
- There are four main types of financial statements.
- Financial statements provide quantitative details and do not account for non-financial and qualitative information.
Objectives of financial statements

Some objectives of preparing financial statements are-
- Present an accurate and fair view of a company
Financial statements provide a comprehensive view of the business.
This is because financial statements record and classify assets, liabilities, profit and loss, cash flow and ownership separately. This classification helps ascertain a company holistically. Financial statements also represent a company’s financial health, net worth and growth prospects.
- Provide sufficient information about the resources
The financial statements provide a summary of all the resources that a business owns.
Based on the financial statements, the management can make efficient decisions suitable for the business. For example, if the balance sheet shows that there are certain unpaid expenses from last year, the management may look at ways to ensure successful payment and closure of accounts.
- Determine the efficiency of the management
The financial statements also reflect the efficiency of management. For example, if sales of a business increase from last year, other factors remain constant, it means that the sales team has made notable efforts.
- Forecast the future
Based on past trends and records of financial data, the management can predict the future growth of the company and plan for the same accordingly.
Advantages of financial statements analysis
- Advantage to the management
The management may look at the financial statements to make short-term and long-term decisions according to a company’s financial position.
- Advantage to the shareholders
Shareholders can decide if they want to remain invested in the company or opt out based on the financial statements and health of the company.
- Advantage to the Government
The government can look at financial statements to determine a company’s tax liabilities and check for compliance.
- Advantage to the employees
Employees may scan financial statements to know how well the company is doing and assess their chances of getting bonuses, increments, and promotions.
- Advantage to the creditors
Using financial statements, creditors can ascertain if the business can pay its interest obligations.
- Advantage to competitors and external agencies
Competitors use financial statements for comparison and analysis.
Disadvantages of financial statements
Some limitations of the financial statements are-
- Ignores qualitative aspect
Financial statements only account for data that can be translated into numbers and quantitative data. They ignore the qualitative aspect of transactions, depicting an incomplete view of the business. For example, labour strikes may impact profitability and revenue. But this reason will not be defined when recording the numbers.
- Window dressing
Window dressing refers to making financial statements more attractive by manipulation. This may, in turn, misguide investors and creditors.
- Biased information
There is a certain level of prejudice involved while preparing financial statements. For example, the management decides if the company will adopt a straight-line or written-down depreciation method. The two methods will give different results and can thus lead to misinterpretation.
Types of financial statements

There are four main types of financial statements
- Balance sheet statement
The balance sheet is a statement that summarises a business’s assets and liabilities for a specified period. It represents the position of the business and also depicts the company’s capital structure.
- Profit and loss statement
The profit and loss statement provides an overview of the expenses and revenue during a specific accounting year. This statement gives an overview of whether the company is profitable or not and helps management take important financial decisions.
- Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement shows a business’s cash inflows and outflows during the year. It helps in determining the liquidity position. The cash flow statement has three main heads- operating activities, investing activities, and financial activities.
- Statement of change in equity
Statement of change in equity depicts the shareholding of the company. It shows the change in retained earnings, equity shares, preference shares, etc.
How to read financial statements?

Financial statements analysis can be done as follows –
- Horizontal analysis
It compares the current financial performance of a company to the base year’s financial performance.
- Vertical analysis
It compares each component in the financial statements to a specific component. For example, in the income statement, the cost of goods sold, administrative expenses, etc., are compared as a percentage of revenue.
- Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis helps assess the company’s liquidity, profitability, and operational efficiency. For example, current assets and current liabilities are used to calculate the current ratio of a business.
- Comparison with competitors/benchmarks
Financial statements can also be compared to the competitors and target benchmarks in order to understand areas where the business can improve.
How are the three financial statements linked?
All financial statements are interlinked. The net profit, recorded at the bottom of the income statement, is linked to the balance sheet and cash flow statement. For example, if a company purchases a piece of machinery, it is recorded as an asset on the balance sheet. However, depreciation is recorded in the income statement, and the cash outflow is shown in the cash flow statement.
Using financial statements to grow your business
Financial statements help ascertain the true value of a company, thereby aiding growth.
As they represent the liquidity position, operational efficiency, future earning capacity, and profitability, financial statements can guide decision-making and enable a company to grow.
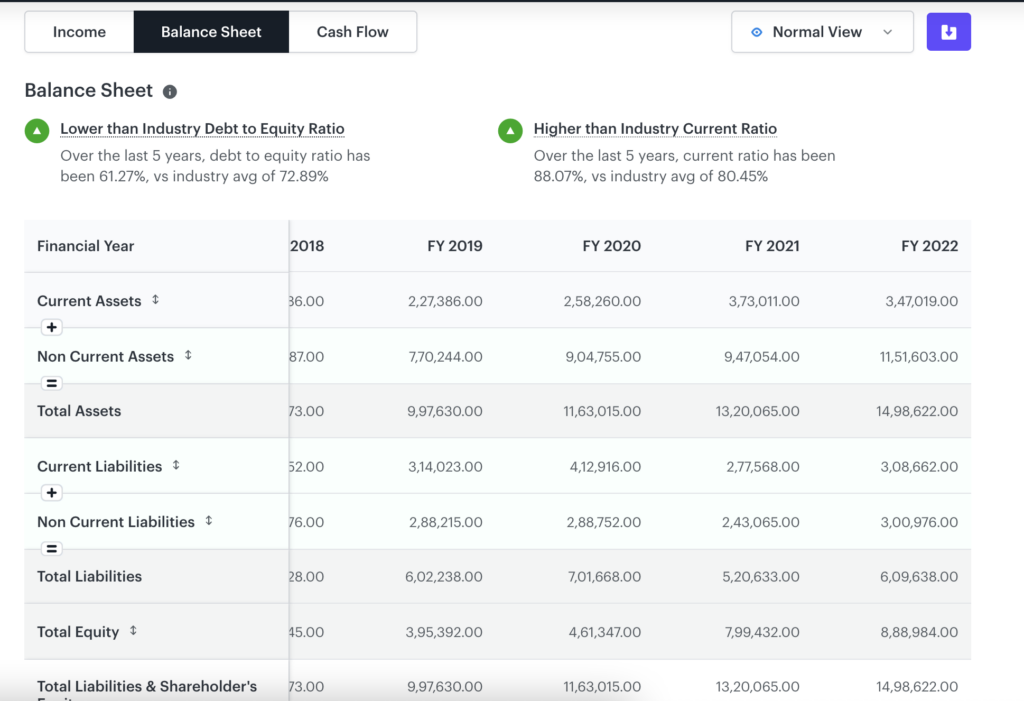
You can use Tickertape to check the financial statements of a company and for peer comparison. Go to any stock page and click on the ‘Financials’ tab. You can view the statements in the ‘Normal’ and ‘Growth’ views. Here’s an example of Reliance Industries Ltd‘s balance sheet –
Conclusion
Financial statements are used to determine the true standing of a company. These statements depict profit and loss, ownership, assets and liabilities, and all necessary financial data. This helps organisations make decisions, forecast, and understand the areas of improvement. Financial statements can be read in various ways. Consult with an expert when reading the financial statements of a company.
FAQs
Did you Like the Explanation?
Authored By:
Aradhana Gotur is a Content Writer with 4 years of experience in personal finance, stock markets, and lifestyle domains. Having recognised the power of words, she uses them to enhance financial awareness among the masses and meet business objectives. One of her greatest strengths is breaking complex concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.



