An endowment is a type of capital structure that non-profit organisations use to raise donations and manage their expenses. Any income received from endowments offers non-profit organisations stability, enables them to make long-term plans, and covers operational and maintenance costs. Let’s dive deeper into the subject to understand endowment.
You will Learn About:
What is an endowment?

The term endowment meaning can be defined as a donation of either cash or property to non-profit organisations that utilises the earnings received for a certain purpose. It is a type of investment capital and is required to be directed towards the organisation’s specific objectives.
An endowment fund is a structure that large non-profit organisations like museums, hospitals, and universities leverage to raise donation income to fund their administrative costs on an ongoing basis. Endowment funds allow non-profits to manage a portfolio of financial assets through which investment returns can be produced. These returns are then leveraged to fund the operations of the non-profit.
The pool of capital is continuously strengthened with additional funds and earnings generated through new donations and reinvested returns. It’s important to note that the principal capital remains unwithdrawn from an endowment fund, and only the investment returns are utilised for operational reasons.
Return on equity: Highlights
- Endowment funds are an investment type held by non-profit organisations like hospitals, universities, museums, churches, universities, and other charities.
- The objective of an endowment fund is to garner investment profits by investing the donated money. Some of the investment earnings are used for operations, and the remaining are reinvested.
- There are three main kinds of endowment funds: term endowments, true endowments, and quasi-endowments.
Types of endowments

There are mainly three types of endowments, the details of which are listed below:
- Term endowment
Like other endowment funds, a term endowment is not everlasting. It’s structured for a specific time, like a fixed number of years, or till an event like the demise of the donor. Once the endowment term expires, the principal amount can be used for administrative and other expenses.
- True endowment
When a donor extends funds to the endowment, it’s stated that they are to be kept perpetually. In fact, true endowments typically involve a legally-binding written agreement stating this term.
You may also like our article on ‘Investments’. Read more on the Tickertape blog.
- Quasi-endowment
The BODs of an endowment fund may authorise the use of reserve funds, financial windfalls, or unrestricted gifts. These additions are characterised as quasi-endowments.
How do endowments work?

Endowment funds are structured in a way that withdrawing, reinvesting, or using capital requires the recipient to follow predetermined guidelines. The good part is the principal amount of the donation stays intact. Meanwhile, earnings from the investment help manage operational expenses and keep the organisation running.
Note: In cases where large donations are received, they are structured differently so that only a certain portion of funds can be used after a stipulated period.
By withholding the release of money from the endowment fund, the managers can leverage the capital, which in turn helps to improve the organisation’s income and expenses.
In fact, endowment funds are often controlled with specific guidelines dictated by the donor(s). This makes it essential for a non-profit to hire a fund manager to help deploy funds as per long-term investment goals. Since these non-profits mostly thrive on endowments, it’s important that these funds get managed in a way that the capital keeps growing and funding the organisation’s expenses.
Requirements for endowments
Fund managers handling endowments need to deal with the push and pull of interests to leverage the investment assets to grow their respective institution, organisation, foundation, or university.
The aim is to sustainably grow the funds by reinvesting the endowment’s income while simultaneously dedicating funds towards the operating costs of the organisation and its goals.
The outline of requirements compiled by the management team involves setting objectives, creating a payout policy, selecting managers, building an asset allocation policy, managing risks systematically, cutting down on expenses, and defining responsibilities.
Most importantly, private non-operating foundations are needed to pay out 5% of their investment earnings on their endowments each year for charitable reasons to maintain their tax-exempt status. On the other hand, private operating foundations are required to pay a whole or about 85% of their investment income.
Advantages of endowments
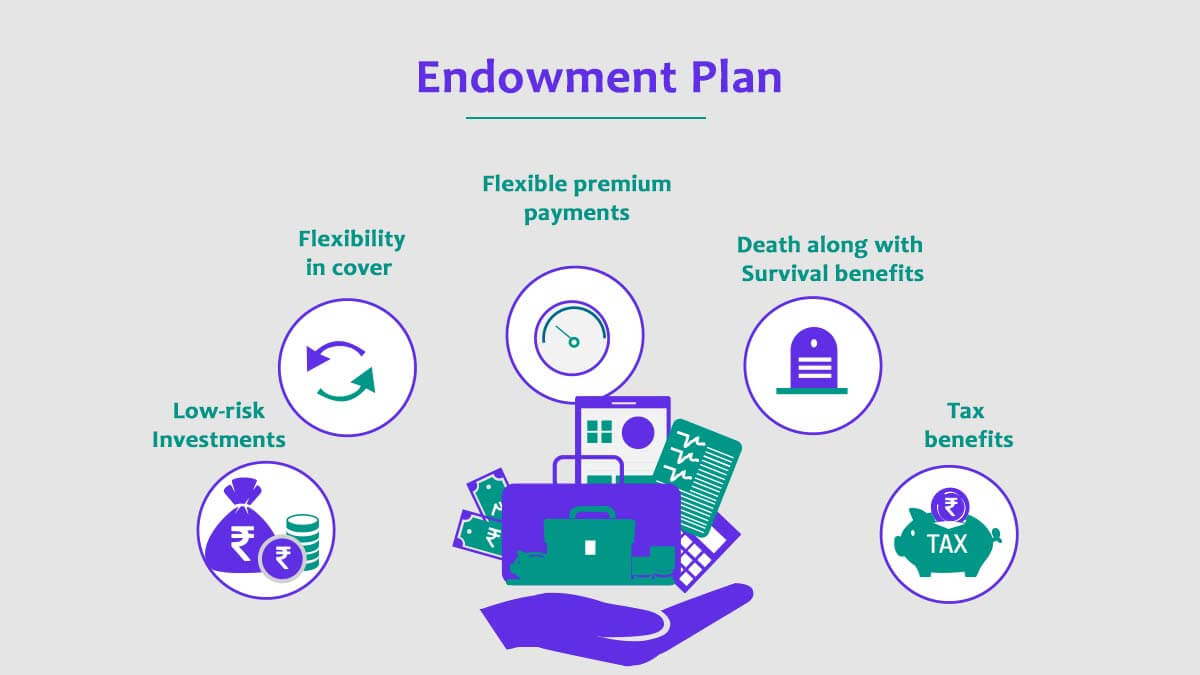
Below, find a list of benefits of endowment plans:
- Offers insurance coverage
- Pays out an assured sum
- Low-risk
- Helps plan long-term saving
- Additional bonuses
Disadvantages of endowments
Below are some of the disadvantages of the endowment plan:
- The protection offered by an endowment plan is for a limited period.
- The premium payable is higher than that of term insurance.
- These policies do not offer convertibility or renewability options that are typically available in term insurance plans.
Example of endowments
A good example of an endowment fund can be a scholarship fund/ sports fund set up in the name of a deceased person through a trust or non-profit organisation.
Breakdown of policies of endowments
Endowment funds are administered by guidelines that outline how their assets can be used. If the non-profit organisation violates the terms in this guiding document, it could experience legal problems.
- Investment policy
The investment policy emphasises why it exists and how it must be managed. This policy document encompasses details like the fund’s investment goals, terms for allocating and reinvesting, recommendations for portfolio monitoring, and benchmarks for assessing performance.
- Fund agreement
The fund agreement is a legally binding document created by the donor that states how the organisation can withdraw and spend the fund’s budget. The non-profit is not allowed to use the fund for other reasons unless the donor agrees.
- Endowment spending policy
The spending policy highlights what investment earnings can be spent annually. For many years now, most endowments have adhered to the 5% payout rule on average, which can even go up to 7%.
Conclusion
With countless investment options available in the market, it has become difficult to identify where and how to invest funds to garner maximum outputs in the future. Endowment funds prove to be a great option as it not only provides coverage for a lifetime but also give a financial goal for the long term.
FAQs
Did you Like the Explanation?
Authored By:
I am a finance enthusiast who loves exploring the world of money through my lens. I’ve been dedicated to building systems that work and curating content that helps people learn.
As an insatiable reader and learner, I’ve spent the last two years exploring the world of finance. With my creative mind and curious spirit, I love making complex finance topics easy and fun for everyone to understand. Join me on my journey as we navigate the world of finance together!



